What is Building Information Modelling (BIM)?
- Shazeb Ali Khan

- Jun 7, 2020
- 5 min read
The requirements of the modern world are increasing day by day thus creating a challenge for engineers to keep creating more optimised and efficient designs with no compromise to the quality. The constraint of space and finance adds more to the complexity of design. With the said challenges, it becomes difficult to visualise all the aspects in one go which leads to the redesign and rework. The revisions in design at last moment or the rework cause a loss of capital and time thus increasing the overall cost of the project. However, this can be avoided if a computer model-based process is created during the design phase which takes all the aspects into consideration and mitigate the problems at the designing phase itself. This model-based process is called Building Information Modelling (BIM). The aspects to be considered in BIM depends upon the need of the client and work scope. These aspects can be civil construction, PEB, HVAC, fire-fighting system, mechanical fabrication, operation and maintenance etc. with desired level of detailing and complexity.
ISO 19650:2019 defines BIM as-
“Use of a shared digital representation of a built asset to facilitate design, construction and operation processes to form a reliable basis for decisions”
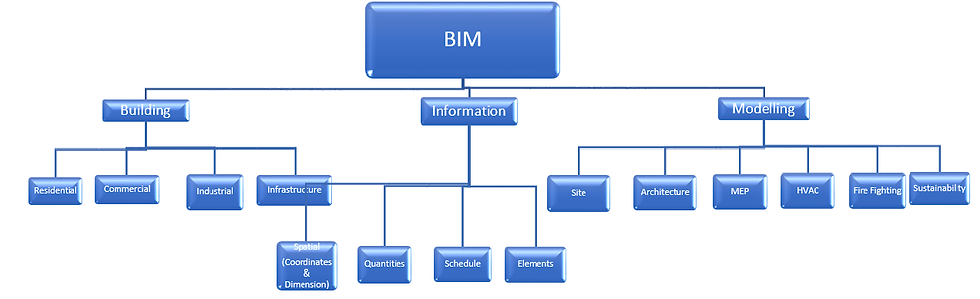
The term Building Information Modelling implies following-
Building- Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Infrastructure.
Information- Spatial (coordinates, dimensions etc.), Quantity, Schedule, Elements (Footings, Beam etc.)
Modelling- Site, Architecture, Structural, MEP, Sustainability.
Why to implement BIM?
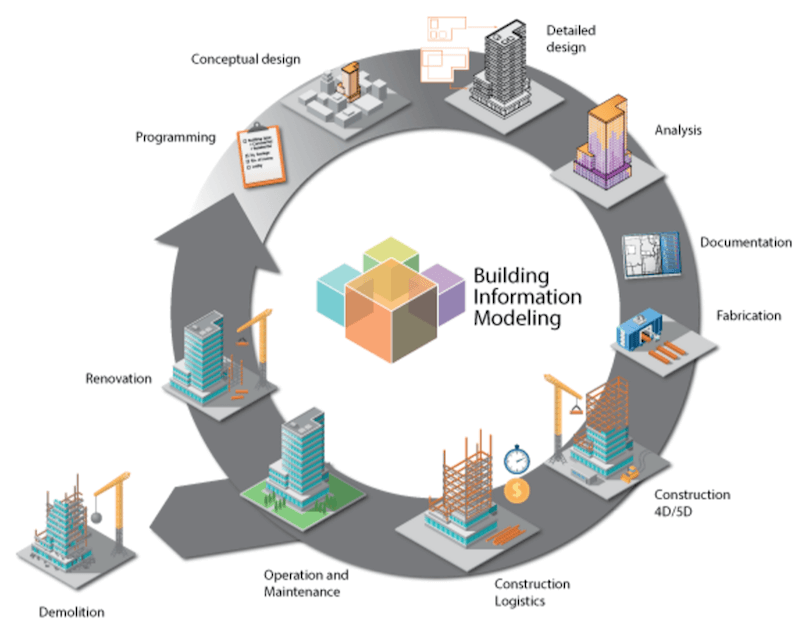
1. To get the accurate representation of the project.
2. To reduce the construction cost by optimising the design and construction materials.
3. To increase the collaboration among stakeholders.
4. To simulate the working conditions.
5. To control the cost of the project.
6. To track the work progress.
7. Clash detection and their mitigation at design phase.
8. To reduce rework.
9. To reduce documentation error.
10. To reduce claims/litigation
Fundamentals of BIM-
1. Levels
2. Level of Development
Levels of BIM-
The levels of BIM are also called Maturity Levels. These Levels indicate the collaboration among the stakeholders during the process of BIM. The mode of sharing information across BIM platforms is also defined I the respective levels. Ranging from zero to three, the maturity levels are defined below-
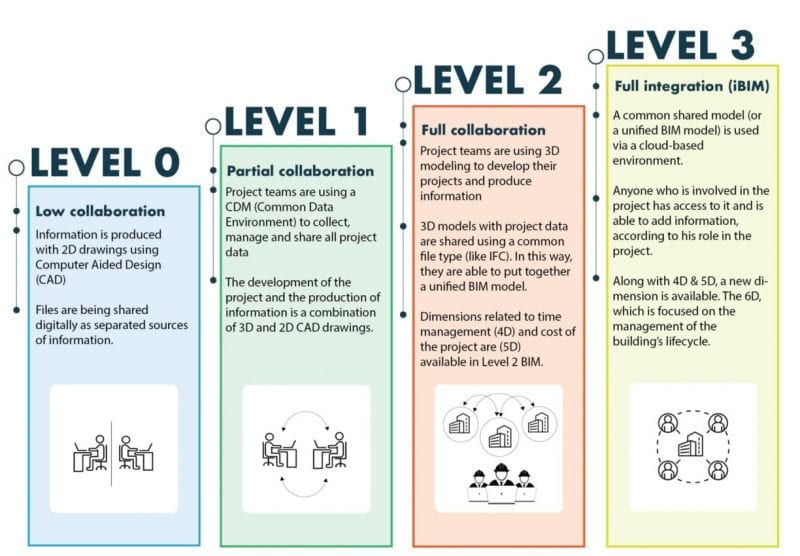
a. Levels 0-
Level 0 operates on the 2D CAD drafting by pen-paper or electronic print. It is an obsolete level and is only used for very small-scale projects.
b. Level 1-
Level 1 may involve 2D or 3D drafting. Data sharing happens electronically. Low or no collaboration between stakeholders.
c. Level 2-
Level 2 promotes collaboration between stakeholders by sharing 3D CAD model. It requires seamless sharing of information between stakeholders through a common file format. IFC (Industry Foundation Class) and CoBie file formats are used for information exchange. At present, Level 2 is being used in the industry.
d. Level 3-
The scope of Level 3 hasn’t been defined yet and is still under research. However, it is said it promotes deeper collaboration among stakeholders with a model stored in a central repository which allow all stakeholders to work on the model simultaneously. Open Data Standards and new framework for data sharing are being developed.
Level of Development (LOD)
The level of Development (LOD) defines the precision of a BIM model. It helps in defining the purpose of the model and quantum of details to be put into the model. The cost of implementing BIM relies heavily on LOD. The higher the LOD, higher is the cost of BIM implementation. The LODs range from LOD-100 to LOD-500. With increase in LOD value, the precision of BIM increase.

a. LOD-100
The LOD-100 model may be created by generic representation. Only conceptual model is created in this LOD and the dimensional parameters (length, area, volume, location, orientation etc.) along with information from model are approximate.
b. LOD-200
This level has elements of the model represented by the generic symbols. Non-graphic information can be attached in the model. The dimensional parameters and any information derived from model are approximate.
c. LOD-300
The model elements are graphically represented with exactly defined details like dimensions, spatial information, orientation. Non graphic information can also be attached with the elements. At present, Indian infrastructure industry is using this LOD. The clash detection can be performed in this LOD.
d. LOD-350
The LOD-350 is similar to LOD-300 except the fact that it has additional details of supports and connections are provided. Thus, it can be said that LOD-350 has element details and its interface with other elements.
e. LOD-400
LOD-400 has element details along with mechanical fabrication, assembly and installation information. Non-graphic information can be added to the elements.
f. LOD-500
LOD-500 model represents the actual details of elements, their assembly and installation. This model is based on the field verified information. Non graphic information can be attached to elements. This LOD is used for operation and maintenance. It is very seldom used in the industry.
Dimensions of BIM-
The Dimensions of BIM represent the quantum of information which has been incorporated into the model. Dimensions can also be called the purpose of BIM. The model can have information related to 3D model, schedule, cost and sustainability. The BIM generally has seven dimensions. However, up to twelve dimensions have been defined by researchers.

a. 1D-
Model represented by a point. Used for existing conditions, regulations, weather simulation etc.
b. 2D-
Model represented by lines in x-y plane. Used for 2D views, plans etc.
c. 3D- Modelling & Information
Model represented in x-y-z plane. Used in BIM element creation.
d. 4D- Duration & Scheduling
When BIM 3D model is integrated with time schedule, the BIM is said to have 4 dimensions. Hence, critical activities along with critical path can be identified. Activities to be crashed can also be identified. WBS can be easily realised in 4D BIM.
e. 5D- Cost
When the cost factor is integrated into model it gives birth to fifth dimension in BIM. The capital expenditure, change in cost, cost tracking, budget allotment can be identified with this model.
f. 6D- Sustainability
The sixth dimension in BIM corresponds to sustainability of the project. It helps in assessing the impact of project on it’s surrounding during the project life. Thus, it is also called project life cycle information. 6D model helps in facility management, estimating electricity consumption, schedule maintenance, optimum configuration, expected lifespan.
g. 7D- Facility Management
The seventh dimension of BIM includes the operation & maintenance part. It tracks asset data such as status, operation/maintenance manuals, warranty information, technical specifications etc. It helps in improving the services provided by the project.
h. 8D- Safety
The eight dimension of BIM takes safety into consideration. It helps is defining the accident-prone spots of the project, evacuation plan etc.
General Workflow of BIM
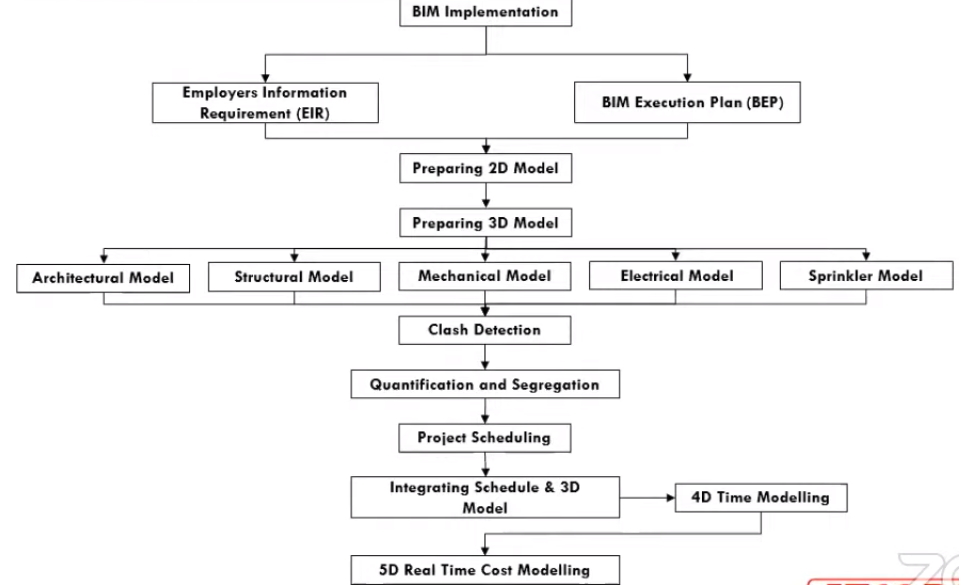
Regulations-
The BIM process has been standardised by the authorities of the respective countries. However, no framework has been prescribed in India for the same.
a. Employer’s Information Requirements (EIR)
It is a pre-tender document setting out the information to be delivered, and the standards & processes to be adopted by the supplier as a part of the project delivery process. It is prepared in accordance with UK PAS 1192-2:2013 & ISO 19650.

For more on EIR-
b. BIM Execution Plan (BPU)
BEP is a plan prepared by the suppliers to explain how the information modelling aspects of a project will be carried out. The BEP Guide can be obtained from http://bim.psu.edu/
BIM Platforms-

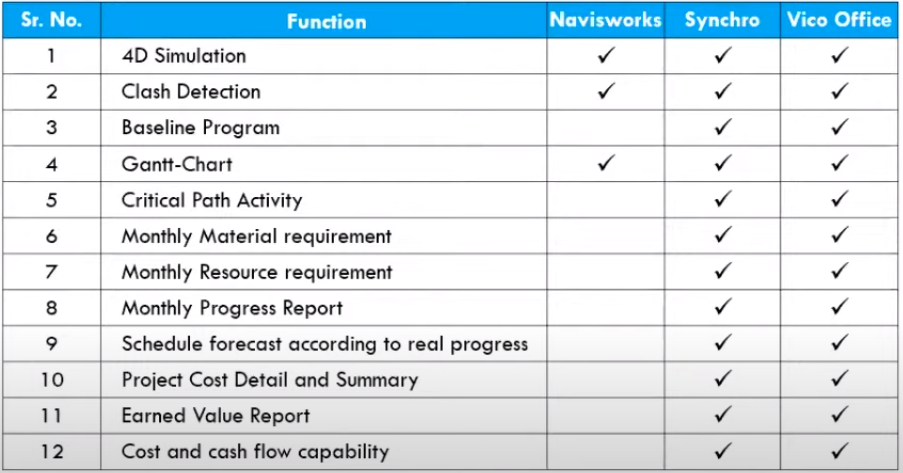
Since BIM is a process thus it needs various software for different operations. For example, 3D modelling can be done using Revit or Navisworks, time schedule can be linked by MS Project or Primavera and cost incurred and other aspects can be linked to model by Synchro or Vico.
The comparison of Navisworks, Synchro and Vico is as follows-
Get BIM softwares from here-
Get Synchro https://www.synchroltd.com/
Get Navisworks https://www.autodesk.com/products/navisworks/overview
Tags-
#bim #bimworld #trend #buildinginformationmodelling #planning #scheduling #projectmanagement #civil #civilengineering #construction #constructionmanagement #synchro #revit #primavera #primaverap6 #autodesk #navisworks #vico #architecture #design #civildesign #hvac #structuredesign #structure
Happy Engineering!
It’s really very informative. I really appreciate your efforts that you have put in creating this blog and spreading knowledge. Good! 👍 Keep it up Shazeb.
Regards
DP Mishra